Identification of mosquitoes and complete information on their types
1. What is a mosquito (carrier)?
2. Types of mosquitoes. (Classification)
3. External structure of mosquitoes.
4. Identification of mosquitoes.
1. What is a mosquito (carrier)?
A mosquito is a vector. And the definition of carrier can be given as follows.
A vector is an insect without a spine that carries the infection in its body and divides it and infects others. which is called carrier.
A mosquito is a flying insect. It has long 6 legs and hard body and bites humans and animals to suggest blood.
Mosquitoes can be distinguished from other insects by the following analysis.
1. They are usually slender flies with the development of proboscis.
2. Palpi are rigid pendulous in shape.
3. 6 legs are long.
4. Antennae tufted in male and slender and long in female.
5. Insects with 6 legs are placed in the class Insecta.
6. In which two wings are visible. It is placed in Dipthera class.
2. Types of mosquitoes. (Classification)
Mosquitoes are almost all over the world. Out of which 255 types of species (pieces) and 14 types of genera are found in India. Of which a total of 58 species of Anopheles mosquitoes are found in India. Out of which only 9 species (Pices) spread malaria. All types of which we will discuss.
genus | Sexes in the World (PCs) | Castes (PCs) in India |
| Anopheles | 420 | 58 |
| Addis | 888 | 111 |
| Culex | 715 | 57 |
| Mansonia | 23 | 04 |
| 34 (genus) | 16 (genus) |
We will get a detailed explanation of the genera and species of mosquitoes found in India. A total of 14 species are found in India. Among them mainly 4 genera spread more diseases. So we will get all types of explanations about 4 genera as per this table.
[1] Anopheles (genus) (carrier of malaria)
More than 58 species of Anopheles genus are found in India. But all those pieces are not carriers of malaria. But out of all those 58 pieces only 9 pieces work as malaria vectors in India. Which are as follows.
| genus | Pieces |
1. Anopheles | Culici facies |
2. Anopheles | Stephensy |
3. Anopheles | Flue via tliese |
4. Anopheles | minimus |
5. Anopheles | Sandaya Cus |
6. Anopheles | Dyrus |
7. Anopheles | Philly Pennies (Naevipus) |
8. Anopheles | Annu laris |
9. Anopheles | Varuna |
[2.] Aedes (genus)
Aedes is mainly dengue. Chikungunya. and finch
There is a carrier (vector) of the virus. Aedes genus has 111 pieces in India. But out of it these 2 pieces as below are mainly dengue. Spreads Chikungunya and Zika disease.
genus | Caste ( Pieces ) | carrier |
| Addis | Egypt | Dengue. Chikungunya. and Zika |
| Addis | Albpicts | Dengue. Chikungunya. and Zika |
Addis | Whitetash |
[3.] Culex (genus)
57 species of Culex genus are found in India. Out of it, only 4 species are carriers as follows. Culex mosquitoes are carriers of elephantiasis (filaria) and Japanese encephalitis.
| genus | Caste ( Pieces ) | carrier |
| Culex | Kwinky Fasciatus | Filaria |
| Culex | Tratenor Rincus | Japanese encephalitis |
| Culex | Vishrnoi | Japanese encephalitis |
| Culex | Sudo Vishrnoi | Japanese encephalitis |
[4.] Mansonia (genus)
4 pieces of Mansonia genus are found in India. Out of which the following 2 pieces (species) are carriers of elephantiasis (filaria).
| genus | Caste ( Pieces ) | carrier |
| Mansonia | Annuli Fera | Filaria |
| Mansonia | Uni Forms | Filaria |
3. External structure of mosquitoes.
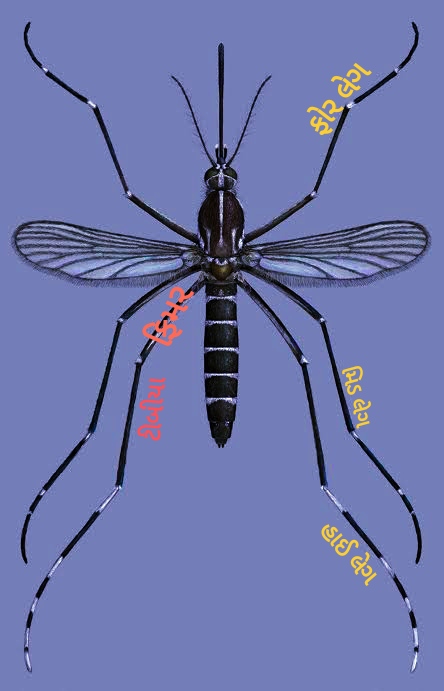
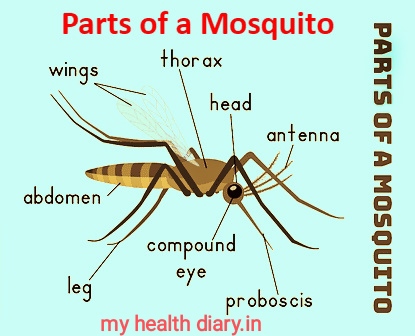
Mosquitoes are relatively small insects of the same genus. 3 to 6 mm in length in many species. Mosquitoes generally range in length from 2 mm to 19 mm. Uniquely, his body is divided into three parts.
1. Head
2. Thorax (torso)
3. Abdomen _
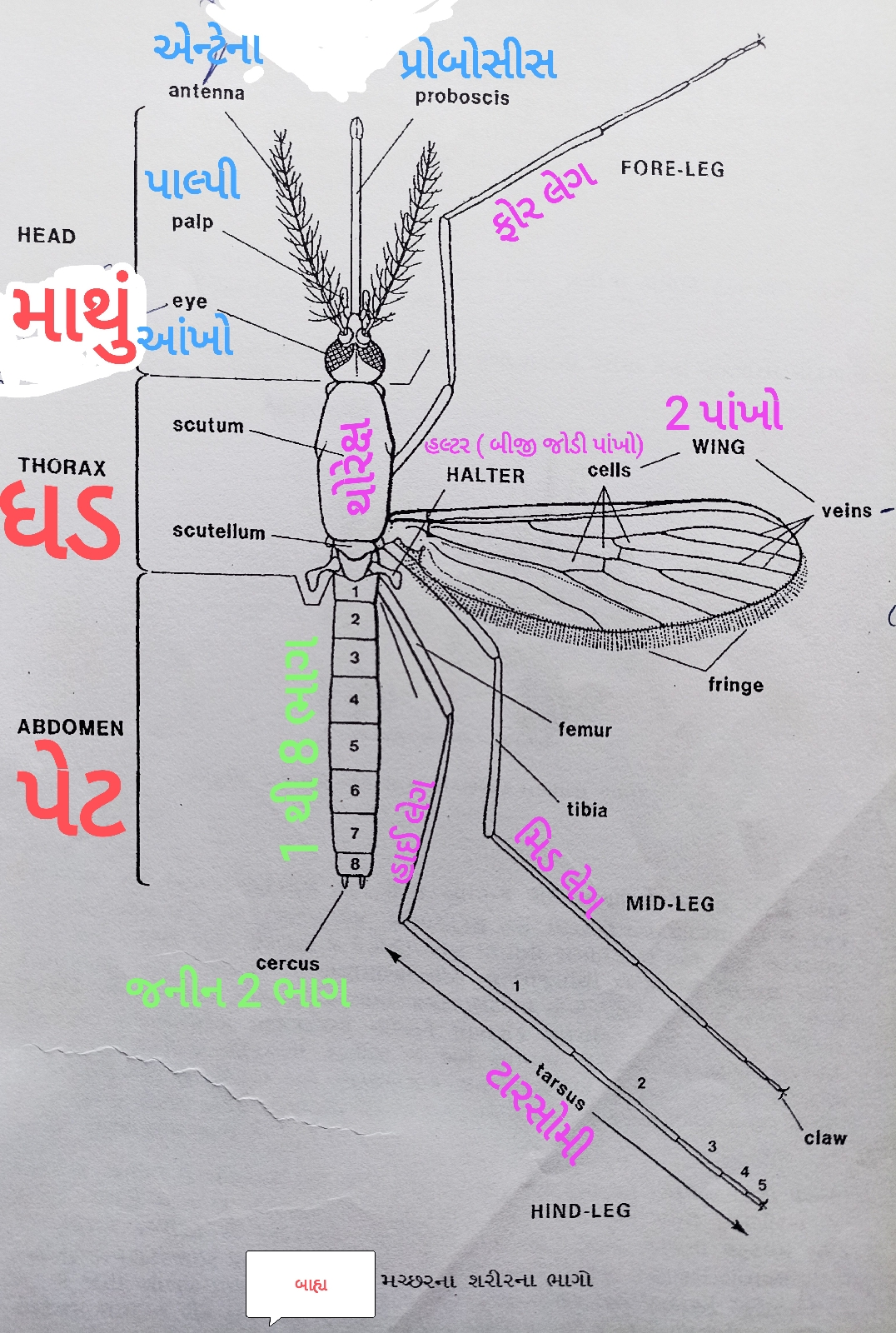
[1.] head (part of head)
The mosquito's head consists of palpi, antennae, proboscis, and compound eyes.
1. Antenna
2. Palpi
3. Proboscis.
4. Compound eyes.
1. Antenna.
To identify mosquitoes, it is necessary to look at their antennae. Is the mosquito male or female? We can tell by looking at its antennae. Antennae have long hairs. which gives a clustered appearance. Mosquitoes can be sexually differentiated by examining the antennae. Antennae in male mosquitoes are tufted. While the antennae of the female mosquito are short and sparsely hairy. In this way, the test of the antennae helps in differentiating male and female mosquitoes.
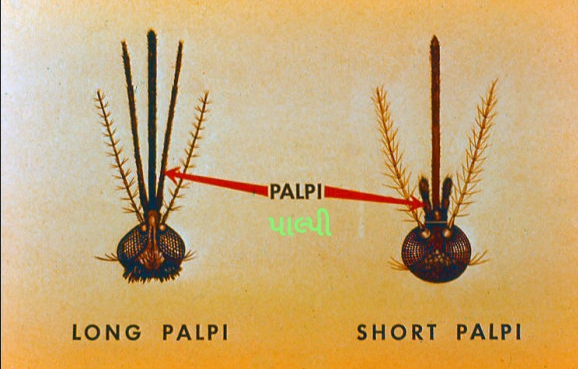
2. Palpi.
A pair of palpi are located just below the antennae and to the side of the proboscis. A pair of palpi helps to identify the species of mosquito by comparison with the proboscis. The palpi of some mosquitoes are smaller than the proboscis. So the palpi of some mosquitoes are bigger than or equal to the proboscis. Based on which mosquito pieces can be known.
Palpi and proboscis are identical in A. phyllis female mosquito. And above the palpi is halesa-shaped. While the palpi of the Culex female mosquito are smaller than the proboscis. Thus, by examining the palpi, it helps to know the species of the mosquito.
3. Proboscis.
Proboscis As shown in the picture above, the proboscis is formed from the middle of the palpi into a long needle-like structure that emerges from its mouth. Through which it works to suggest human and animal blood.
But males do not bite. The largest part of the mouth is the labium . which is in the shape of a long tube. which is at the end of a pair of small lids. To those who is known as .In all parts of the mouth the labium is found circularly attached to each part. which acts as a protective covering. All parts remain attached to the Xaat throughout life, when separated during the blood sampling process, or when separated as part of a test. The uppermost abdominal structure labum is thin and scaly pale with its tropical surface. Between this upper roof (labrum) and the lower canal are five needle-shaped structures. The lower pair of the anterior maxilla and the upper pair of mandibles are the normal teeth. However, in Anopheles it is extremely thin and eventually forms the only toothless tool-like structure. This is known as hypothyroidism .
When the body parts of the female mosquito are attached to the skin of the host's body, the labium, which does not pierce the skin, twists and retracts. So the pair of mandibles, the mapil pair prepares the labrum and the hyprorhyx to pierce the skin of the host. In the anterior part of the thorax are the salivary glands. which is drawn down again by the hand from the triangular gland. Saliva contains anti-hemostatic enzymes such as apyrase that produce hematomas in the skin. And arranges to collect blood from that location. Anticoagulants are also mixed in mucus. which prevent blood from clotting and prevent the problem of pulling in the mouth. Because it is mixed in the labum and other root perforating parts. Anesthetic substances help reduce the pain of mosquito bites. thereby reducing the host's defense response,
4. Compound eyes .
Each mosquito has a pair of compound eyes. Compound eyes are a set of many eyes. Many eyes can fix vision in one place.
[2] Thorax (torso)
The thorax part of mosquito can also be divided as follows. There are 3 parts in the thorax (trunk) of mosquitoes. Also there are 2 pairs of wings. And there are total 6 legs in 3 pairs.
1. Thorax
2. Wings.
3. Legs
[1] Torso (thorax)
Mesothorax
Prothorax
Metathorax
The thorax in mosquitoes consists of three parts. Mesothorax , prothorax , metathorax especially on the back . The pairs of legs are attached from each part. Mesothorax. Most cover the thorax in the form of transparent shiny and hard skin that is covered with scales.
The arrangement of scales and the pattern formed on the hard skin is very important for identifying the mosquito species. Which is known as paratergite . A small oblong square or triangular sclerite is situated on the sputellum between the mesothorax spark and the base of the wing. Presence or absence of scales and setae on the paratergite is common. Which is very important for species identification of mosquitoes. Scales covered on thorax and glabrous behind. Can be white, brown, or black or any color.
[2.] Wings.
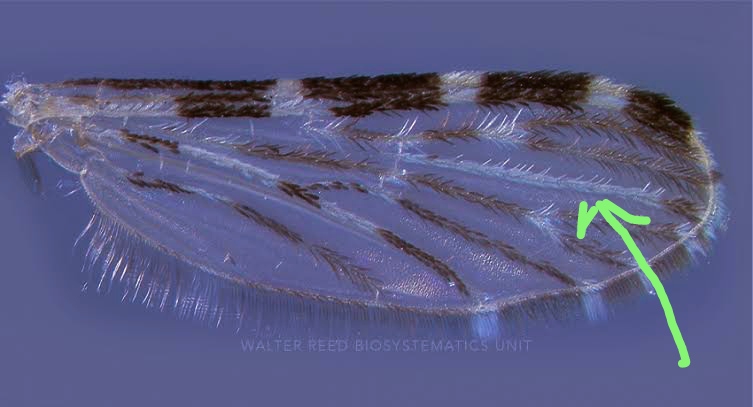
The wings of mosquitoes are narrow in length and proportion. And the number and arrangement of wing veins is the same in all mosquito species. A total of 6 veins are located inside the wings. In which 1.3.6 Vance Divide is not. 2.4.5 Veins are divided. Veins are covered with scales. Which are usually brown, black, white or creamy yellow. The shape of the scales and the pattern on them show significant differences between species and species .
Mosquitoes have 2 pairs of wings. The second pair of wings is called the halter . The humming sound of the mosquito in flight is due to this second pair of wings. This second pair of wings helps in keeping the balance of the mosquito.
[ 3 .] Foot
Mosquitoes have long and thin legs and are covered with scales. which are usually brown, black, or white. which are decorated with carvings. Often circular. The last part of the foot (tarsus) is claw-like.
( Fore leg from prothorax , mid leg from mesothorax , high leg from metathorax .) There are 6 legs in total. Each leg has a total of 7 parts. (1. femur, 1. tibia, and 5 tarsomes) To identify the species of mosquitoes, it is necessary to look at the prints on their legs.
[3] Abdomen
Abdomen of mosquitoes is made up of 10 segments. But primarily, only 7 to 8 segments are seen. And 2 parts of the mosquito's genitalia are found and there are a total of 10 segments (parts).
Without food, mosquitoes are thin and densely built. which is called unfed . But the female mosquito takes a blood meal (female only). Then the stomach swells to a very large extent. And it is found in the shape of oval red blue. Which is called freshly fed . . When the abdomen of the mosquito appears half red and half white it is called haf gravid . When the eggs are fully developed in the abdomen, the full abdomen appears white. After which no red is seen that is called gravid .
4. Identification of mosquitoes.
Before identifying a mosquito, it is necessary to know its habits.
【 Biting Behavior 】
■ Anthropophagic ( Athropophagic ) = Mosquitoes that bite humans are called athropophagic.
■ zoophagic / zoophilic = mosquitoes that bite animals are called zoophilic.
■ endophagic = Mosquitoes that bite indoors are called endophagic mosquitoes.
■ Exophagic = A mosquito that bites outside the house is called an exophagic mosquito.
【Behaviour of Rest】
■ endo philic (indo philic) = mosquitoes resting inside the house are called endo philic.
■ Exo philic = A mosquito that rests outside the house is called exo philic.
To identify the species of mosquitoes, it is necessary to examine the following parts of the body of mosquitoes.
● Head and head parts : antennae; Palpi .and scales on the body
● Thorax (chest): The scales on the chest should be drawn.
● Wings : arrangement of decorated veins and color of scales
● Foot : The parts and joints of the foot end
● Abdomen : arrangement ornamented with scales.
1. Anopheles (carrier of malaria)
2. Aedes (Carrier of Dengue Chikungunya. Zika)
3. Culex ( carrier of elephantiasis (filaria) and Japanese encephalitis)
4. Mansonia ( carrier of elephantiasis (filaria).
1. Anopheles (carrier of malaria)
■ A scientist named Meigen identified the Anopheles mosquito in 1818.
■ A scientist named Ronald Rose proved that malaria is caused by mosquitoes. It is the discovery of India.
A total of 58 species of Anopheles genus are found in India. But out of them only 9 species (species) are carriers of malaria. It is necessary to identify the species of Anopheles found in our area. identify from
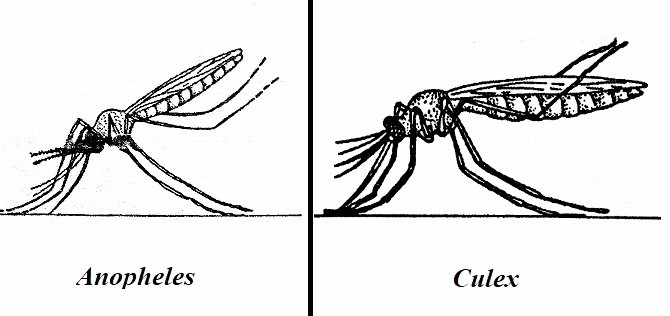
To identify the Anopheles genus, first look at its head. If you see the same palpi as its proboscis, then it is Anopheles. Its planting method is planting at an angle of 45°.
■ Proboscis and palpi of Anopheles females look identical. While the palpi and proboscis of Anopheles mail (male) are similar and the palpi is visible from the top.
1. Anopheles stephensi. (urban)
◆ A large white patch appears on the thorax.
◆ Spelliges (white spots) are visible on its hind legs (femurs and tibias).
◆ Forefoot tarsals are black.
◆ The anterior part of the palpi (apical) is white and the sub apical is uniformly white. White dots are seen in the black part below it.
◆ Both apical white and sub apical white are similar in palpi. While in the pre-apical, the black color is small.
◆ White dots are visible in the black part below the white of the subapical in the palpi.
◆ Generally takes food (blood) in 10 to 12 hours of night.
◆ Commonly consumes blood of both humans and animals as food.
◆ Ability to fly in urban areas is limited. But in rural areas it can be up to 3 km.
◆ Anopheles stephensi is found all over India. Scattered shadows are found in the northeast. Except the upland area of the north.
◆ Commonly lives in human dwellings and cattle sheds. May rest on objects hanging behind curtains in human dwellings.
◆ Anopheles stephensi is more common in urban areas. 15 to 20% transmit malaria.
◆ It is raised in place of wells. Rooftop tanks. Floor tanks. Rooftop rainwater harvesting sites and swimming pools in underground water storage tanks. In rural areas they lay their eggs in water tanks called kothi.
2. Anopheles culicifaces (Rural)
A. phyllis cuanlicephalus causes 60 to 70% of malaria in most rural areas. Which is more zoophilic (prefers animal blood more) mosquitoes.
● The thorax of Cunlycyphas is golden in color when viewed from above.
● Its survival style is similar to that of Culex mosquitoes. Sits flat on the wall. Culex lives like a mosquito, so it is named as Culexaceae.
● It is the smallest mosquito. All its legs are completely black in color .
● The apical white and preapical black (black) parts are exactly the same when looking at the palpi. The sub apical white is smaller than the apical white.
● White spots are not visible in the tarsals of the forelegs.
● The 3rd vanes in the wing are black.
● The innercosta (at the beginning of the wing) of its wing is white. There are more than 3 white black dots on its wings.
● Cunlysifacies is found throughout India but not reported in Andabar-Nicobar and Lakshadweep Islands.
● Sand puddles generated by springs and animal footprints in Culinaryfacies breeding grounds. Bridges over rivers. A canal for irrigation. In rice fields. Banks of wells and lakes. In the monsoon, more expansion is observed in the current flowing in the sandy banks.
● It rests during the day in human habitations and cattle sheds.
● Cunlyciphasis usually consumes food throughout the night. But usually from 7 pm to 4:00 am the eclipse is more intense.
● Cunlycyphasis is zoophilic (blood-sucking activity on animals) in nature. While in high abundance, humans also consume relatively large amounts of food.
● The flight capacity of Cuunlysiphas is approximately 1 to 3 ki. is m.
3. Anopheles fluviatilis.(Hill area).
◆ The apical pay band is white and the pre apical black band is identical.
◆ The 3rd vanes in the wing are white.
◆ Innercosta wing tip is black.
◆ Legs are black.
◆ Costa with more than 3 white black dots on sub costa.
◆ Widely found in hilly areas.
◆ Breeding location slow flowing springs. A canal for irrigation. and places around it. Raised in paddy fields and shallow wells. Often this species is washed away in heavy rains.
◆ Habit of rest Human habitation and cattle rest in manger.
◆ The time of taking food is usually entering the house at sunset. And the activity of taking food is completed before midnight from 9:00 to 11:00.
◆ The feeding habit of fluviatilis is generally anthropolic (prefers human blood). Zuliphylli is also found in North India.
◆ The ability to fly has a limited capacity.
4. Annularis.
● The apical pay band is white and the pre apical black band is identical.
● 3.4.5 segments total white in tarsomy of hind high leg leg. So the Negro looks like he is wearing white gloves.
● It is a mosquito of total black color. There is a mosquito with white gloves.
5. Subpicts (not carriers of malaria)
The subspecies mosquito is not a carrier of malaria but is found in many areas of Gujarat.
● The apical pay band is white and the pre apical black band is identical.
● Front no fore leg is bigger. And there is a white stripe on the tarsal of the fore leg. There is a large band on the fore leg.
● There are more than 3 white spots on the costa of the wing.
● There is no white dot (trough) in the hind legs. are black.
● Raindrops are produced in water.
. Aedes genus has 111 species in India. But out of them the following 2 pieces are the main carriers of dengue. Carriers of Chikungunya and Zika virus. which spreads disease. To identify Aedes, one has to look at the thorax. Addis Egypt is the main carrier of urban - semi-urban and rural areas.
1. Aedes aegypti (carrier of Dengue, Chikungunya and Zinka).
Aedes aegypti is found in large numbers in Gujarat. Addis Egypt is the main carrier of urban - semi-urban and rural areas. 90% of whom do not rest in a drug-sprayed area. These species have a great preference for consuming human blood. It is anthropophilic.It has the nature of taking blood during the day.
◆ Tiger (white stripes on legs and body) is a mosquito.
◆ Is a container breeder.
◆ He does not sit on the wall .But prefers to sit on things that are more stimulating.
◆ Mosquitoes are sensitive to torches.
◆ Thorax should be seen to identify Aedes. On both sides of the thorax of Aedes aegypti, a crescent shaped white mark is visible.
◆ White bands ( patta o ) are seen on their legs.
◆ It is a day biter mosquito. 7 to 11 am is the best time to bite. After 5 pm.
◆ Acute feeding habit: The feeding habit of Aedes aegypti is extraordinarily complex. Arvatan 52 is involved in female mosquito laying eggs. Attacks several individuals repeatedly over a short period of time for a blood meal.
◆ Dengue. Chikungunya. Yellow fever. And is a carrier of West Nile virus. But in India dengue is Chikungunya only)
◆ Mating sites: Aedes aegypti prefers to breed in man-made water containers such as those that hold water for more than a week. i.e. in uncovered water containers (cement tanks-rooftop tanks, floor tanks), house roofs, non-consumable dry materials, outdoor debris like bottles, tyres, buckets and coconut husks etc.
◆ Resting place: Aedes aegypti mosquito usually rests in places like house, office, business premises, tire, umbrella hanging on black cloth in the dark corner of the house. In the lower part of the house, behind the bed and cooler, in the boot, in the boot, behind the curtain, etc. and in other dark places that are rarely found on the wall.
◆ Flight capacity and extension: Aedes have a flight capacity of up to 100 meters. but can fly up to 400 m. Aedes can spread to new places in different areas by passive transport.
2. Addis albicans
Aedes aegypti is found in large numbers in Gujarat. But Aedes albicans is not found in Gujarat.
● Aedes albpictus is identified by a long white spot on its thorax.
● Tiger (white stripes on legs and body) is a mosquito.
● White bands ( patta o ) are seen on their legs.
3. Aedes whitetash.
◆ 3 dots are seen on the right and left sides of the thorax.
◆ Tiger (white stripes on legs and body) is a mosquito.
◆ White bands ( patta o ) are seen on their legs.
3. Culex ( carrier of elephantiasis (filaria) and Japanese encephalitis)
57 species of Culex genus are found in India. Out of it, only 4 species are carriers as follows. Culex mosquitoes are carriers of elephantiasis (filaria) and Japanese encephalitis.
> The palpi of Culex female mosquito are smaller than the proboscis. While the palpi of the male Culex are larger than the proboscis and tooth-shaped. have And the antennae are clustered.
> Abdomen has white and black stripes.
> Culex mosquitoes bite at night. The humming mosquito that keeps you awake at night is the Culex.
1. Culex quinquefasciatus
● The palpi of the female Culex mosquito are smaller than the proboscis. While the palpi of the male Culex are larger than the proboscis and tooth-shaped. have And the antennae are clustered.
● Abdomen has white and black stripes
Mating : Females usually do not feed before mating. (12 to 24 hours after emergence) Mating time takes place at dusk.
Extended average flight capacity is 2 to 3 km. is But the ability to fly is limited.
Feeding behavior: Ingestion of food in 24 to 48 hours after mating during daylight hours. Usually late at night in the third watch of the night. It is endophagic and exophagic in nature.
Host Preference: Extremely anthropophilic (prefers to bite humans) but also frequently feeds on birds and to a lesser extent dogs, cats and pigs, but also feeds on the blood of other domestic animals.
Rest feature: Enters the house for food during the day. And rests on the walls of dark corners of the house, on hanging objects, on moldy garbage, in boots, moths in the closet or under the table in the bathroom, etc., which are endophilic and endocagesic in nature.
Gonotropic cycle: In a favorable environment (25 to 30°C >90° RH) one gonotropic cycle is completed in 2 to 4 days. Before completing each cycle, the female requires a blood meal.
Seasonal Influence: Two-phase influence is observed throughout the year in abundance in northern parts of the country. (February to March and September to October)
Additional Incubation Period and Longevity: Research by Rao and Iyengar below 24°C and above 34°C
Temperature (Vaucheria bancrofti) inhibits the growth of Culex quinquie caciatus According to Khalil the filarial parasite is 23 to 24° in 20 days and 29° to 39. Temperature matures in 14 days.
The average lifespan of a female mosquito is between 15-45 days.: The lifespan is shorter during adverse climatic conditions. Comparatively, life expectancy is higher during rainy seasons.
4. Mansonia ( carrier of elephantiasis (filaria).
4 pieces of Mansonia genus are found in India. Out of which 2 pieces (species) are carriers of elephantiasis (filaria).
Dispersal Activity : Not strong flying nature. Flies quietly for short distances. Catches quickly like a sandfly.
Food nature: During the night period, the first and second watches have a food nature.
Host Selection: Man. annulifera is highly anthropocilic. Mansonia unicormus is more succulent.
Resting Habit: Man.annulifera is endophilic and endophagous in dark corners of the house.Man.indiana rests in mangers and other outdoor places.
Seasonal influence: The highest density of men.uniformis occurs in January, May, September and December. However, infective and infective mosquitoes (both species) are found throughout the year. Is the density of M. uniformis higher during June and August when Salvinia host plants are completely replaced by Pistia?
My health diary .In









































ટિપ્પણી પોસ્ટ કરો